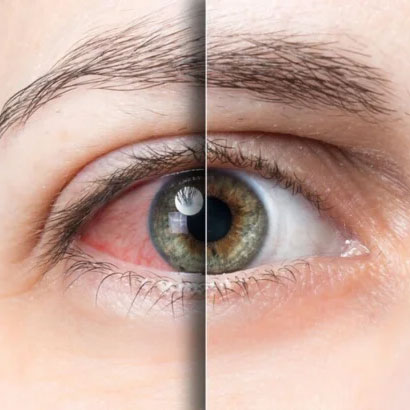
How is uveitis diagnosed ?
Diagnosis involves a dilated eye exam where eye drops widen the pupil for a thorough
examination. Additional tests may be required to identify underlying causes. Your doctor may order various blood
investigations and eye scans (Optical coherence tomography, Optical
coherence tomography angiography, Fundus fluorescein angiography).
What is the treatment of uveitis ?
Treatment primarily involves steroids to reduce inflammation and prevent vision loss.
Steroids may be administered through eye drops, oral pills, eye injections or implants.
Regular eye exams are essential to monitor for potential side effects such as cataracts and
glaucoma, which are associated with steroid use.
Few patients may also require oral antiobiotics and immunomodulator therapy.
Rarely, advanced uveitis may require vitreo-retinal surgery.
Your treatment plan will depend on several factors — like which part of your eye is affected, and other health
conditions you have. You can work with your doctor to find the right treatments for you.